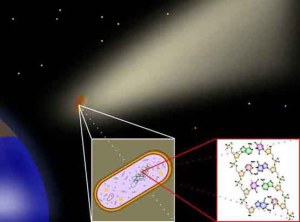
Panspermia – the idea that life exist across the whole Universe and it can be transferred from one location to another.
In August 1996, teams of scientists found in Antarctica a meteorite that contains fossils blasted off from the surface Mars about 15 million years ago. Than 4kg Stone labeled ALH84001 contains balls of carbon originating from micro-organisms while they were alive. Several tests for organic material have been performed on ALH84001 and amino acids and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) have been found.
 The late Nobel prize winner Professor Francis Crick, OM FRS, along with British chemist Leslie Orgel proposed the theory of directed panspermia in 1973. A co-discoverer of the double helical structure of the DNA molecule, and gen HAR1, which separates us from animals, for which Crick found it impossible that the complexity of DNA could have evolved naturally.
The late Nobel prize winner Professor Francis Crick, OM FRS, along with British chemist Leslie Orgel proposed the theory of directed panspermia in 1973. A co-discoverer of the double helical structure of the DNA molecule, and gen HAR1, which separates us from animals, for which Crick found it impossible that the complexity of DNA could have evolved naturally.